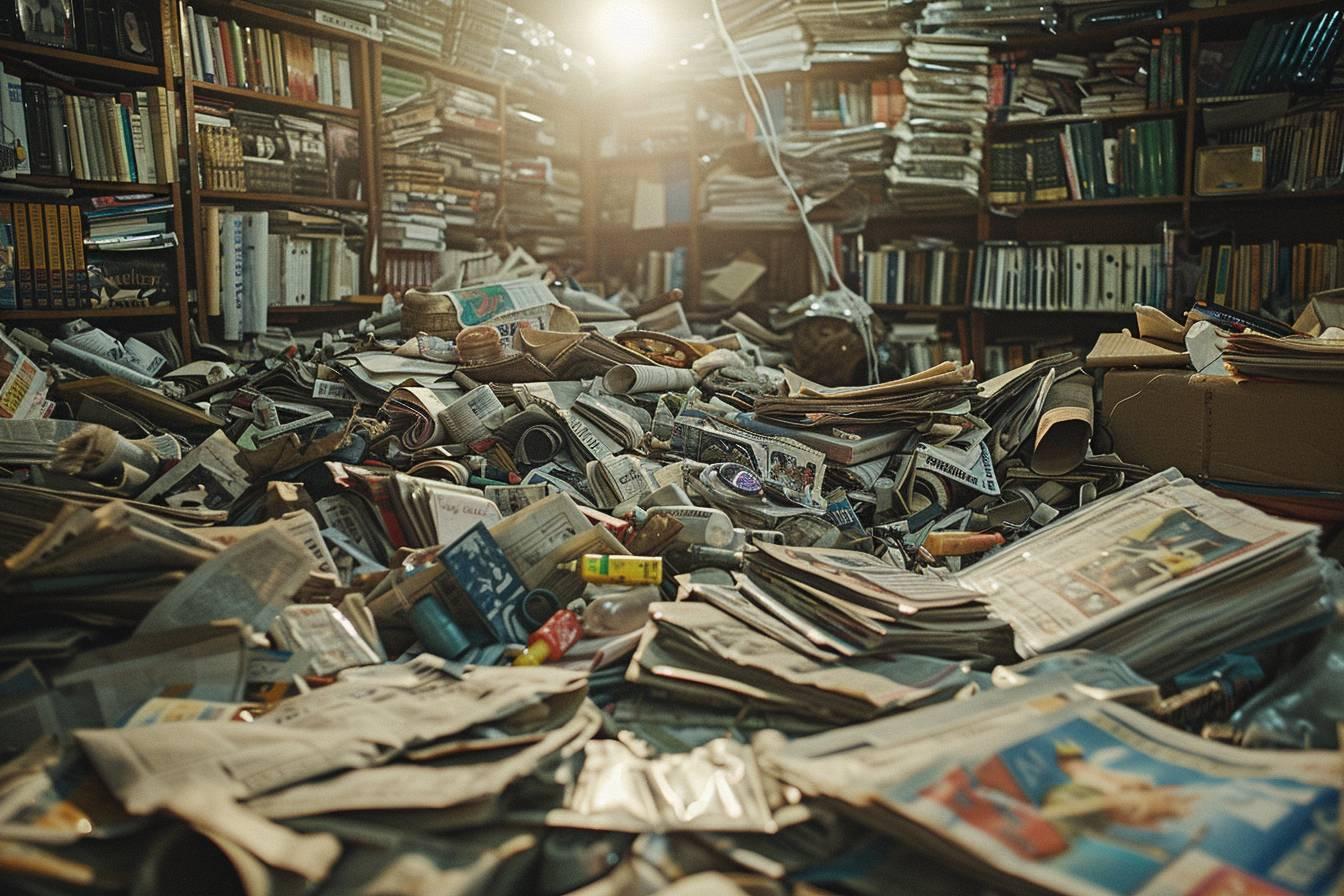
Syllogomania, also known as compulsive hoarding disorder, is a complex psychological condition that affects millions of people worldwide. This article delves into the intricacies of syllogomania, exploring its causes, symptoms, and treatment options. By understanding this disorder, we can better support those who struggle with excessive accumulation and develop effective strategies for managing this challenging condition.
Unraveling the causes of syllogomania
The roots of syllogomania are multifaceted, stemming from a combination of genetic, neurological, and environmental factors. Research suggests that individuals with this disorder may have distinct brain patterns that affect their decision-making processes and emotional attachments to objects.
Genetic predisposition plays a significant role in the development of syllogomania. Studies have shown that people with first-degree relatives who exhibit hoarding behaviors are more likely to develop the disorder themselves. This genetic link suggests a hereditary component to the condition, although the specific genes involved are still being investigated.
Neurologically, individuals with syllogomania often display abnormalities in brain regions responsible for decision-making, attention, and emotional regulation. Neuroimaging studies have revealed differences in the prefrontal cortex and anterior cingulate cortex, areas crucial for executive function and emotional processing.
Environmental factors also contribute to the development of syllogomania. Traumatic life events, such as the loss of a loved one or experiencing material deprivation, can trigger hoarding behaviors. Additionally, growing up in a household where hoarding was present or where possessions were given excessive importance can influence an individual’s relationship with objects later in life.
The interplay between these factors creates a complex web of influences that shape the onset and progression of syllogomania. Understanding these causes is crucial for developing effective treatment strategies and prevention measures.
Recognizing the symptoms of compulsive hoarding
Identifying syllogomania can be challenging, as the symptoms often develop gradually over time. However, there are several key indicators that can help in recognizing this disorder. The most prominent symptom is the excessive acquisition and difficulty discarding items, regardless of their actual value or utility.
People with syllogomania often experience intense distress at the thought of parting with their possessions. This emotional attachment can lead to the accumulation of items to the point where living spaces become cluttered and unusable. The hoarding behavior typically extends to various categories of objects, including :
- Newspapers and magazines
- Clothing and accessories
- Books and documents
- Household items and appliances
- Collectibles and memorabilia
Another hallmark of syllogomania is the impairment of daily functioning. As clutter accumulates, it can interfere with basic activities such as cooking, cleaning, and sleeping. In severe cases, hoarders may create narrow pathways through their homes, risking their safety and health.
The social impact of syllogomania is also significant. Individuals with this disorder often experience strained relationships with family and friends due to their hoarding behaviors. They may feel embarrassed about their living conditions and avoid inviting people into their homes, leading to social isolation.
To better understand the severity of syllogomania, mental health professionals often use assessment tools like the Clutter Image Rating Scale. This visual scale helps evaluate the extent of clutter in different areas of the home :
| Clutter Level | Description | Impact on Daily Life |
|---|---|---|
| 1-3 | Mild clutter | Minimal interference with daily activities |
| 4-6 | Moderate clutter | Some impairment of living spaces and routines |
| 7-9 | Severe clutter | Significant obstruction of living areas and daily functioning |
Recognizing these symptoms early can be crucial in seeking timely intervention and support for individuals struggling with syllogomania.
Effective treatment approaches for syllogomania
Treating syllogomania requires a multifaceted approach that addresses both the psychological and practical aspects of the disorder. While there is no one-size-fits-all solution, several evidence-based treatments have shown promise in helping individuals manage their hoarding behaviors and improve their quality of life.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is widely considered the gold standard for treating syllogomania. This therapeutic approach focuses on identifying and challenging the thought patterns and beliefs that drive hoarding behaviors. CBT for hoarding typically involves :
- Cognitive restructuring to address distorted thoughts about possessions
- Exposure therapy to gradually reduce anxiety associated with discarding items
- Skills training in organization, decision-making, and problem-solving
- Motivational interviewing to enhance commitment to change
In addition to CBT, Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT) has shown promise in treating syllogomania, particularly for individuals who struggle with emotional regulation. DBT incorporates mindfulness techniques and teaches skills for managing distress and interpersonal relationships.
Medication can also play a role in treating syllogomania, especially when co-occurring conditions such as depression or anxiety are present. Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs) have been found to be effective in reducing hoarding symptoms in some individuals. However, medication is typically used in conjunction with therapy rather than as a standalone treatment.
For severe cases of syllogomania, intensive treatment programs may be necessary. These programs often involve a combination of individual therapy, group sessions, and hands-on decluttering assistance. The support of professional organizers or cleaning services can be invaluable in helping individuals make progress in managing their living spaces.
It’s important to note that treating syllogomania is often a long-term process that requires patience and persistence. Recovery is possible, but it typically occurs gradually over time. Supportive family members and friends can play a crucial role in the treatment process by offering encouragement and understanding.
Moving forward : Hope and support for those affected by syllogomania
While syllogomania can be a challenging and often misunderstood disorder, there is hope for those affected by it. Increased awareness and research have led to better understanding and more effective treatment options. Support groups, both in-person and online, provide valuable resources and a sense of community for individuals struggling with hoarding behaviors.
Organizations such as the International OCD Foundation offer educational materials, treatment referrals, and support networks for people with syllogomania and their loved ones. These resources can be instrumental in helping individuals take the first steps towards recovery.
As society becomes more aware of syllogomania, efforts to reduce stigma and promote compassion are crucial. By fostering understanding and providing access to appropriate care, we can help those affected by this disorder reclaim their lives and living spaces.
Ultimately, overcoming syllogomania is a journey that requires courage, support, and perseverance. With the right combination of professional help, personal commitment, and a supportive environment, individuals with syllogomania can make significant progress in managing their hoarding behaviors and improving their overall well-being.

